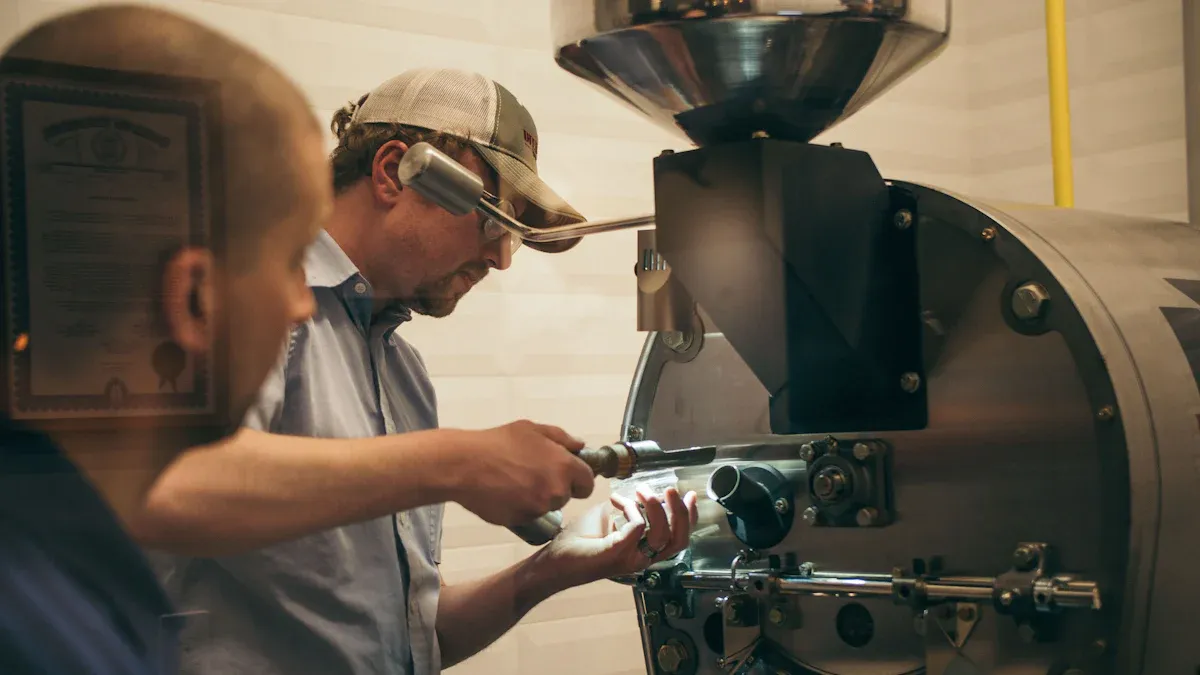
Cutting Return Rates is crucial for new product development, as it directly impacts profitability and brand reputation. This case study illustrates how one company achieved a return rate of less than 1% from initial prototype to final product. Their success hinged on a robust foundational product strategy, which integrated early and collaborative quality assurance processes. This strategy meticulously vetted the core product design, transforming their operational approach. Companies adopting such a strategy, especially with automated quality checks, frequently realize up to a 30% reduction in defect-related costs. This demonstrates the significant benefits of prioritizing the foundational product early in the development cycle. Thorough validation of their core product was paramount, ensuring its integrity. This foundational product strategy established a new benchmark, guiding every stage of development with meticulous scrutiny of the core product. This strategic blueprint yielded exceptional results, underscoring the unique success achieved through a strong foundational product.
Key Takeaways
Fix problems early to stop product returns. Check quality from the start of making a product.
Test your product often. Use feedback from users to make it better before selling it.
Work with suppliers from the beginning. Make sure materials are good and meet quality rules.
Use test runs to find and fix issues. This makes sure many products can be made well.
Keep getting ideas from users. Use these ideas to make the product better all the time.
The Challenge: High Returns & Strategic Shift
Early Product Return Issues
Many returned products hurt a company’s money. They make costs go up. Companies deal with complex return systems. This includes shipping back items. It also includes checking products. This work needs special staff. Worker costs go up. Teams handle return requests. They get items ready to sell again. This takes away from growth. Money flow slows down. Refunds are given for unsold items. Returned products often lose value. This is true for seasonal items. Selling them at full price is hard. Trash from packaging adds up. So do costs for new items.
Many things cause high returns. This happens when products are new. Products fail if they do not meet needs. They also fail if sold to the wrong people. A product needs to be special to do well. Being late to market can also cause failure. Market demand changes. Or new rivals appear. Bad prices or high making costs cause issues. These problems start early. A strong mvp development strategy helps find risks. It helps fix them. It makes sure the product meets real needs. This early action helps with cutting return rates. A good mvp checks product ideas early. It stops expensive mistakes later.
Moving to Proactive Quality
Companies often change how they fix problems. They move to preventing issues. Reactive work fixes problems after they happen. It focuses on fixing damage. This way often costs more. This is due to quick fixes. It also causes delays and bigger problems. Reactive ways are not good. They involve fast choices. They use temporary fixes. This can stress out teams. It also risks unexpected failures.
Proactive work looks for problems early. It takes steps to stop them. This way looks to the future. It focuses on stopping issues. It plans and lowers risks. Proactive ways usually cost less over time. They cut down on emergencies. They make work better. This leads to more efficient work. It gives more control. It helps new ideas grow. Proactive work lowers risk. It finds and stops threats. It makes customers happier. This is because products are good. This long-term plan helps growth. Testing well before selling is a best practices example. Doing regular system checks also shows this. A strong mvp development strategy is key here. It makes sure quality is there from the start. Companies clearly define their mvp. They test each mvp version. They check it against market demand. This repeated mvp development strategy improves the product. It builds quality into every step. This mvp development strategy makes sure the product meets user hopes. It also finds problems early. This is a best practices way for product success. Each mvp gives helpful ideas. These ideas make the product better. It makes sure it fits market demand. The mvp is like a live plan. This mvp development strategy stops future problems. It makes sure the mvp is strong.
Proactive Quality: From MVP to Production
This part shows how they built quality. It was done from the start. Kingham‘s team has much experience. They have worked for over 15 years. They own more than 70 patents. This knowledge helps them plan ahead.
MVP Validation & DFM Integration
The company checks its mvp very well. This makes sure products are good. It also makes users happy. They clearly define each mvp. They pick key goals for testing. They know their users well. They know what users need. They see how their product helps. Studies help them see other products. They find special spots in the market. They make changes based on user feedback. This mvp development strategy makes sure the product sells.
Better tests for new products are key. Accelerated Life Testing (ALT) finds problems early. This happens when they design the product. It lets them make changes. This is before the product sells. ALT saves money. It stops recalls and fixes. It makes products last longer. Products tested with ALT work well. They work for their whole life. This makes customers happier. ALT makes sure products meet standards. This helps companies win.
User acceptance testing (UAT) is also very important. Alpha testing is the first full test. Company staff does this test. It checks if the software works as needed. Beta testing comes after Alpha testing. Real users test the software. They check how it works. They look at how it feels to use. Black box testing checks inputs and outputs. It makes sure the software works for users. This helps with alpha and beta testing. Operational Acceptance Testing (OAT) checks if work flows smoothly. It sees if the software is ready to use. This full mvp development process checks with users well.
The mvp development strategy uses many tests. Usability testing looks at how users feel. It finds hard or confusing parts. They watch people use it. They record screens. Heatmaps show where users look. This tells them what to change. A/B testing compares two product versions. It finds which one works better. They look at how many people leave. They also look at how many buy. Beta testing groups use the product. They find problems. They confirm good features. This makes the product better for users. It checks if people want it.
Getting user feedback well is important. They use emails and in-app messages. Surveys ask users if they are happy. They see how the mvp is liked. They check their first ideas. They make the product better with user ideas. Talking to customers helps. They learn about their thoughts. They ask about experiences and hopes. This needs clear goals. It needs a curious mind. This user testing and feedback collection is a good way to work.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) show what works. They use ideas from users early on. They use numbers as the mvp grows. Examples are how much users use it. Also, how long they stay. Tools like Google Analytics track website visits. Tools like Hotjar show more about users. Setting clear goals helps the mvp testing. It makes sure every step fixes a real user problem. Picking the right numbers fits the mvp stage. This turns numbers into helpful actions. Finding problems early saves money. It stops wasting money on features. Features that users might not like. A single-feature mvp focuses efforts. It focuses on the most important feature. This makes development faster. It also makes it cheaper. These are good ways to build an mvp.
Design for manufacturing (DFM) starts early. DFM greatly lowers defects. It cuts costs and delays. Key ideas include picking materials. This means choosing cheap materials. They must work with current ways of making things. Making designs simpler means fewer parts. This stops mistakes and saves money. It aims for balance and sameness. Making things for current machines is key. It avoids needing special tools. Setting real limits ensures it can be made. Modular design breaks products into parts. These parts are easy to make. They fit together easily. These ideas make products better. They make work run smoother.
Using DFM ideas means working together. Design and making teams work as one. DFM experts join early. They join when products are designed. This teamwork finds making problems early. It makes sure the product is best for making. This process lowers errors and defects. It makes products better quality. Kingham’s CNC machines are key for DFM. They have over 100 machines. They make things with great accuracy. Modern CNC machines are very precise. Some are even more precise. This is for complex parts. Parts that need exact sizes. This accuracy makes the functional prototype match the final product. Using design for manufacturing saves a lot of money. It makes products better. It makes development faster. It makes production faster. It makes the whole mvp development process smooth. Quality checks are a final DFM idea. It means making parts easy to check. It adds ways to stop errors. It makes sure quality is always the same.
Early Supplier & Material Qualification
Working with suppliers early stops problems. The company finds what materials are needed. They also find what services are needed. They think about quality and if it’s available. They also think about being green. This helps them pick suppliers. They set clear quality rules. Suppliers must meet these rules. This includes papers and industry rules. Early supplier checks gather basic facts. This includes what they sell. Also, their name and money status. They send out a Request for Information (RFI). This asks for details. It asks about their skills and quality checks. They check supplier answers. They check against their rules. They focus on quality and delivery times.
Finding and checking suppliers first is step one. They check for quality and rules. They use market studies and databases. They check their name and money status. They also check if they follow rules. Grouping suppliers by importance is key. They call some suppliers very important. Others are standard. This risk-based way decides how much to watch them. They get first papers. This includes company info and papers. They ask for info and plans. They set the work scope and quality hopes. They check quality systems and papers. They approve good suppliers. They make deals and quality papers. They bring in and train suppliers. They watch and manage supplier work. They check quality often. They approve or stop using suppliers as needed. This makes transitioning from prototype to production smooth.
A quality check finds bad suppliers. This lowers risk. Asking for a product sample helps. It checks if a supplier can do the job. This is before making many products. A ‘golden sample’ is a perfect example. It sets a quality standard. It helps fix problems. This stops defects. They give suppliers a quality book. Or a checklist. This is the main guide for rules. It has product details. It has limits for defects. It also has checking and packing rules.
Material checks make products reliable. They make them work well. Mechanical tests include shaking and hitting. Also, pulling tests. These check how products handle stress. Environmental tests include heat and wetness. These check how they work in different weather. Electrical tests check for interference. It makes sure devices work without problems. Chemical tests look at what things are made of. It checks for purity. It checks if materials work together. Functional tests check if a product does its job. Reliability tests check how long a product lasts. It finds ways it might break. Software tests include unit and system tests. Regulatory tests make sure rules are followed. Life cycle tests include endurance tests. This guesses how long it will work.
Kingham’s OEM/ODM plan helps teams work together. It also checks quality with partners. This plan saves money. It also lets them make more products. This is by buying together. And by making things better. It helps with new ideas. It helps with custom products. ODM teams know new tech. They use new plastics and materials. Surface treatments like anodizing make things stronger. They also make them look better. Kingham knows materials well. For things like “brake-system-parts.” And “Popular Finishing Types and Surface Styles for Aluminum.” This is a big plus. Custom design tools let brands add their needs. This keeps making things efficient. The plan also makes things fast to market. Better development makes things quicker. Tests done at the same time find problems early. Quality and rules are most important. Full quality systems make products work well. Statistical checks watch key things. This stops defects. Kingham’s mvp development best practices ensure quality from the start.
Making Sure Things Are Good: From Test to First Product
It takes careful steps to go from a test product to a real one. Keeping things high quality is very important. This part shows how they make this change smooth and good.
Great Test Runs & Quality Checks
Test runs are key to check the mvp. They find design flaws. These were missed before. They also find problems with making many items. Test runs check how products work. This is in real-world settings. This makes features better. They show problems in making things. This helps fix them. It makes mass production smoother. Test runs show how many items are bad. They show quality problems. These were not clear before. They let them check everything. This proves the design is good. It stops quality problems. This is before making many items.
All teams must work together. This makes the change smooth. This includes buying, engineering, making, quality, and product managing. Working together fixes problems fast. Special goals guide test runs. These include testing many units. They also find making problems. Watching bad rates is important. So is how well things are made. And how resources are used. The test size should be big enough. It needs to give good info. It must also be easy to handle. This is usually 10%-20% of the first order. Getting facts is key. It shows if the test run worked. It helps understand trends. It shows what to make better. This helps make smart choices. It helps decide about making many items.
Quality control is vital. This is when going from test to mass production. It makes sure products are the same. It makes them reliable. This keeps the brand good. It keeps customers happy. Makers use strong quality checks. This meets set rules. Differences between test and real products can cause flaws. It can cause market failures. This shows why strict quality checks are needed. Auto-check systems lower flaws. They keep product quality high. This is true for all making.
Kingham uses full quality checks. This is through the whole making process. Pre-Production Inspection happens before making. It checks raw materials. It checks parts. This stops bad materials from being used. In-Process Inspection happens during making. It finds flaws as they happen. This allows quick fixes. Final Quality Inspection happens after making. It makes sure the product meets all rules. This is before shipping.
Kingham uses set ways of doing things. They follow clear rules for each step. This lowers human mistakes. Regular machine care stops problems. This keeps product quality good. Full worker training makes sure quality is met. Workers find and report problems.
Auto-making systems make products better. They lower flaws. Auto systems do tasks the same way every time. This lowers mistakes. It makes more good products the first time. Kingham’s auto-making and testing make things more exact. They make them more steady. They stop human tiredness. They use the same check rules. These systems find flaws. These flaws are not seen by eye. They are very exact. Auto-check systems make making faster. They find flaws early. This lowers wasted materials. It stops costly making delays. Real-time watching allows quick changes. This lowers stopped time. It keeps making steady.
Keeping quality high is hard. This is when going from test to real product. Small flaws in test products are okay. They can become big problems when making many. Being the same size is hard to keep. Small test product changes cause big making problems. This is when making many. Material actions can be hard to guess. This is when making many. Materials may act differently in large amounts. This needs changes to how things are made. Tool wear and trust are worries. Tools working well in test products. They may wear out fast in mass making.
Kingham fixes these problems. They build quality into their product design. They ask important questions:
Can we check this feature?
Can all rules be met?
What tests are needed?
Is this design too risky? Can it be simpler?
Are there size limits? These are for making and finishing.
Does the making team have all info? This is for good making.
Designing good parts is more than just making them. It makes sure rules can be checked. It makes sure they can be met always. Kingham sets quality rules. They set check plans. This is before the first making run. They use ways to pick samples. They use in-line testing. They use quality checks. They get facts. This sets quality goals. This guides future making. They keep good records of changes. These changes happen during small making. This helps for full making. They make the design better for large making. They fix how parts fit. They fix how they look. They think about material changes. They use user ideas. They make processes better. This makes things work best. It stops mistakes. They change how work flows. They make tools better. They improve quality control. They change suppliers. They make shipping better. They put money into small making. This is during the test phase. This gets good info. This is before full making.
Feedback Loops & Ready to Launch
Getting feedback is key. This makes products better all the time. Kingham gets customer feedback. They use many ways. These include in-app feedback. They use surveys. They use customer help talks. They also use user research. They use interviews. They use focus groups. They use many ways to get feedback. They get feedback at different times. They ask specific questions. These are clear and based on the situation. They use open questions. These get detailed feedback. They use structured questions. These are easier to check. They involve team members early. This builds understanding. It helps them think about users.
They check facts from user feedback. They sort feedback. This includes problems using it. It includes requests for features. It includes bugs. They decide what is most important. This is based on how often it happens. It is based on how bad it is. It is based on business goals. They use theme checks for written feedback. They combine this with number facts. They find common ideas. They find trends. They look for patterns. They group similar comments. This shows bigger trends. It shows user needs. They combine facts. They mix number feedback with written feedback. This gives a full picture. It leads to useful ideas.
They act on the ideas. They turn checked feedback into clear advice. This goes to the product team. They share ideas with the right teams. This happens through reports. It happens through workshops. It happens through design thinking. They put solutions in place. They add ideas into making products. This makes updates. It fixes problems. It adds new features. This is a repeating process. They finish the loop. They tell users about actions taken. This builds trust. It makes users more involved. This early user check helps make the mvp better. The mvp goes through strong user testing. It goes through feedback. This makes sure the mvp meets market needs. The mvp’s success needs constant user checks.
A full launch checklist makes sure all quality steps are met. This includes watching abilities. It makes sure problems can be found. Problem-solving ability fixes issues fast. Security checks handle weak spots. They handle who can access what. Performance checks make sure the system handles expected use. Full papers give help for support. They give help for use. Kingham checks CI/CD pipelines. They make sure auto deployments work. They test ways to go back. They write down disaster plans. They set clear Service Level Goals. They test for failures. They confirm backup systems. They confirm failover systems. They do load testing. This acts like expected traffic. They plan for future growth. They check auto-scaling. They make runbooks. These show common failure situations. They give step-by-step fixes. They give tips for finding problems. They explain service info. They explain what it depends on. From test to real product, each mvp step builds quality. The final mvp is ready to launch. This full way makes sure the mvp is good.
Results: Sustaining Sub-1% Return Rates
Quantifying Return Rate Reduction
Kingham’s Impact on Return Rate Metrics
Kingham’s good quality systems helped a lot. Their precise making skills cut down returns. For example, they used DFM and automated QC. Return rates then fell from 3.2%. This was during early testing. They stayed below 1% in all later builds. This success was not by chance. Kingham watched data in real-time. They used quick feedback. This fixed problems before making more. This kept returns below 1%.
Real-time data helps teams. It finds making problems right away. This keeps production on track. Monitoring systems show problem spots. This helps move resources. It cuts down on waste. Seeing how machines work helps quality. It makes it easier to fix flaws. It meets rules. Real-time watching keeps everything together. This is from design to making. It includes scheduling and checks. It connects teams. They share product data. This helps them work better. Live data from machines goes to teams. This checks if things can be made. It checks quality and growth. This feedback makes choices better. It makes machines last longer. It makes development faster. This means fewer errors. It means more good products. It makes making things more profitable.
Benefits Beyond Reduced Returns
Kingham’s Role in Delivering Broader Value
Kingham’s early action did more than cut returns. It saved money. It made customers happier. It made the brand look better. Working with Kingham helped launch products faster. It lowered warranty claims. Working together helped make things better always. It made products last longer. Kingham knows about OEM/ODM solutions. This gave a plan for new products. It kept quality high. It made work efficient. This plan also helped make new versions. It allowed quick changes. This was based on market feedback. The client could launch new products with trust. Each product had Kingham’s strict quality checks. This made every product strong in the market.
It is possible to cut down how many products are returned. The goal is to have less than 1% returned. This must happen from the first model to the final product. This needs smart and early quality control. Good plans include design that works together. It also means strict testing of the mvp. Getting suppliers involved early helps. Strong test runs are important. Always listening to what users say is key. This makes moving from a test model to a real product easy. Spending money on quality early helps a lot later. It lowers risks. It makes more good products. It cuts extra costs. Happy customers buy again. They become loyal. This makes the brand stronger. Kingham supports these early quality plans. Their skill makes each mvp better. Kingham is a good partner to reach these high goals. They make sure the mvp is strong.
FAQ
How does checking quality early help lower product returns for an mvp?
Checking quality early finds and fixes problems. It fixes design and making issues. This happens before many items are made. It makes sure the mvp works for people. This way of working early lowers how many items come back.
Why is “Design for Manufacturability” (DFM) important for a good mvp?
DFM puts making ideas into the design. This makes fewer mistakes. It makes designs simple. It picks the right materials. DFM makes sure the mvp can be made well. It makes sure it is good quality.
How do test runs make sure the mvp is good before it fully launches?
Test runs check how things are made. They do this on a small scale. They find problems in making and putting things together. This step makes the process better. It makes sure the final product is always good. It shows the mvp is ready to be made a lot.
Why is talking to suppliers early important for a good mvp?
Talking to suppliers early makes sure materials are good. It makes sure they are there. It sets clear rules for quality. It lowers risks in getting parts. This early talk helps the mvp stay strong. It helps it move to being made.
What does constant feedback do to make the mvp better?
Constant feedback from users and teams helps make the mvp better. It finds things to improve. It checks new features. This back-and-forth process makes the mvp change. It makes sure it meets what users need.