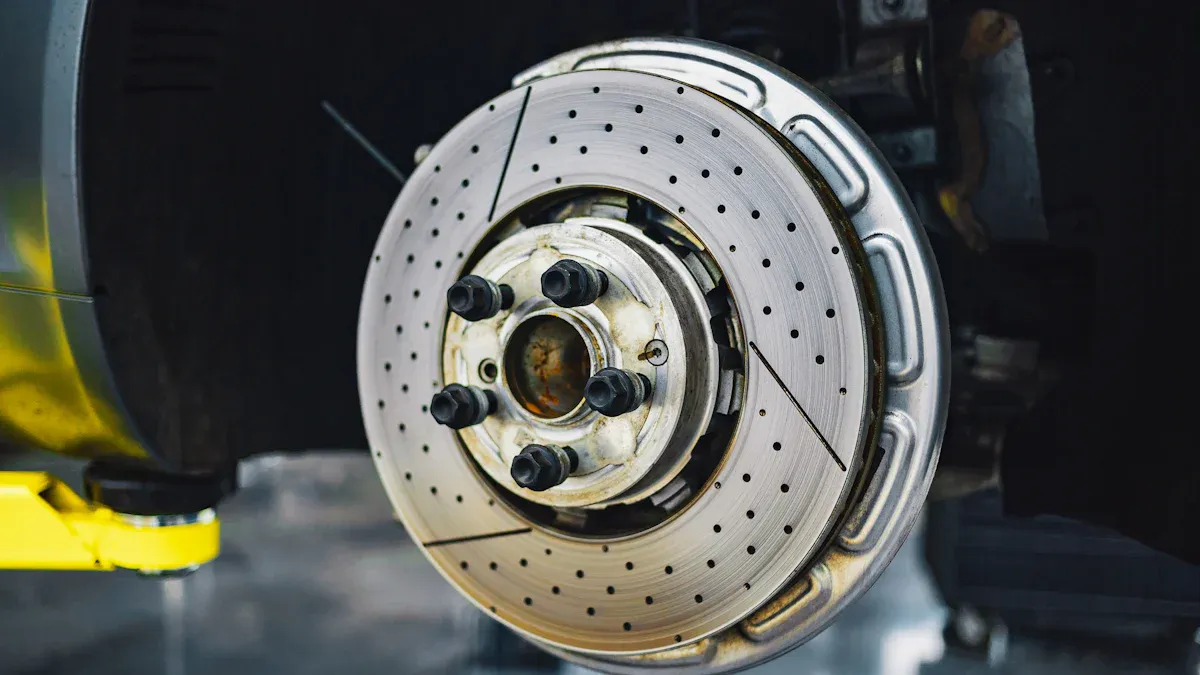
In the car industry, quality control is crucial for ensuring long-term reliability of brake parts. These components must perform effectively to keep you safe while driving. Poorly manufactured brakes can lead to significant issues, such as extended stopping distances and an increased risk of brake fade under stress.
To maintain high safety standards, manufacturers conduct rigorous testing and adhere to international safety regulations. These measures help minimize the likelihood of defective parts, ensuring that every brake system operates efficiently. The table below illustrates how various quality control steps contribute to vehicle safety:
Quality Control Measure | Impact on Vehicle Safety |
|---|---|
Rigorous Testing | Ensures braking systems are reliable and function properly |
Adherence to International Safety Standards | Reduces the risk of defective parts compromising safety |
Post-Market Surveillance | Monitors product performance to identify safety issues |
Warranty Analytics and Field Failure Analysis | Aids in enhancing quality and safety over time |
Batch-Level Traceability | Facilitates quick recalls in the event of safety concerns |
Your safety on the road depends on the long-term reliability and effectiveness of these critical components.
Key Takeaways
Quality control is very important for safe brake parts. It makes sure brakes work well and follow safety rules.
Using good materials like ceramic and semi-metallic helps brakes last longer and work better.
Testing methods, like checking hardness and heat resistance, are key for making sure brake parts are safe.
Improving manufacturing processes helps make better quality parts and lowers defects in brake components.
Certifications like ECE R90 and IATF 16949 are key for making sure brake parts meet safety standards.
Precision Engineering for Brakes

Design’s Role in Reliability
Design is very important for brake parts. It helps make sure they work well for a long time. You want your brakes to work the same way in different situations. Here are some design features that help with this:
Design Feature | Importance |
|---|---|
Quality of Materials | Using strong materials like good cast iron and special steel makes them last longer. |
Manufacturing Processes | Careful casting, machining, and heat treatment make them stronger and reduce problems. |
Quality Control Protocols | Strict testing methods lower the chances of problems and ensure brakes work well. |
Sustainable Practices | Eco-friendly manufacturing shows a commitment to quality and lasting value. |
By focusing on these design parts, makers can create brake systems you can rely on.
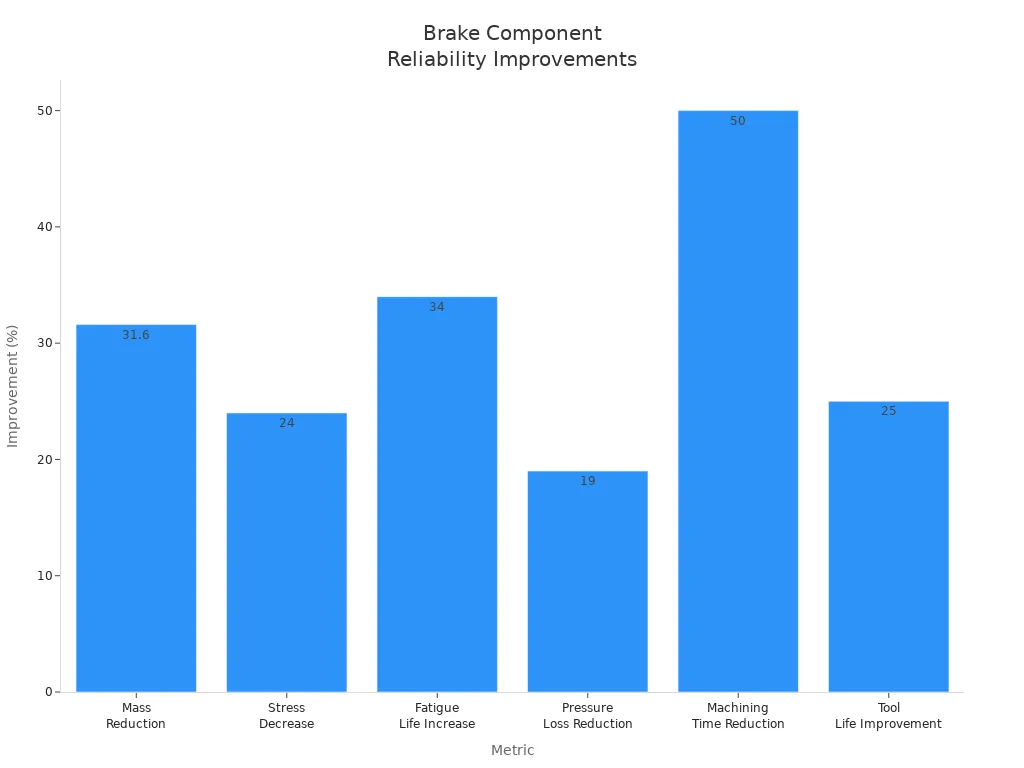
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Advanced manufacturing methods greatly improve how OEM brake parts are made. These methods make sure each part meets high quality standards. Here are some key techniques used in making these parts:
Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Automation | Fully automated machines with ±0.3mm tolerance control make production more precise. |
Robotics | Using robots lowers human mistakes and speeds up brake disc production. |
Additive Manufacturing | Uses materials like boron carbide and molybdenum disulfide to boost brake part performance. |
Advanced Material Engineering | Uses special steel-ceramic mixes for better heat resistance and wear. |
Quality Control Techniques | Non-destructive testing and computer checks make sure strict standards are followed. |
These advanced methods not only make brake parts more reliable but also improve how well they work. This means you can expect better stopping power and longer-lasting brakes from your systems.
Material Selection for Quality
High-Quality Materials
Choosing good materials is very important for making brake parts last a long time. The materials you pick affect how well your brakes work and how safe they are. Here are some materials often used in OEM brake parts:
Ceramic brake pads: These pads work really well and last a long time. They are made from a ceramic mix that gives great braking power, even when it’s hot. They also make less dust, which keeps your wheels cleaner.
Semi-metallic brake pads: These pads have metal fibers like copper and steel. They are strong and can handle heavy braking. However, they might create more brake dust and can be louder than ceramic pads.
The features of these materials, like how hard they are and how well they resist heat, greatly influence how brake parts perform. For example, harder materials can give better braking force but might wear down rotors faster. The table below shows how different hardness levels affect performance:
Brake Pad | Hardness (HRC) | Performance Implications |
|---|---|---|
BP1 | Highest (44) | Best braking force, high wear resistance, but may cause rotor wear |
BP2 | Lowest (38) | Less abrasive, moderate performance |
BP3 | Moderate (44) | Lowest braking force, smoother performance, less wear potential |
Performance Testing
To check the quality and strength of brake materials, manufacturers do many performance tests. These tests make sure the parts meet safety rules and work well in different situations. Here are some common tests done on brake materials:
Material Composition Testing: This test checks how strong and durable the brake material is through chemical and metal analysis.
Hardness Testing: This measures how well the material resists bending, which affects wear and heat resistance.
Dimensional Accuracy Testing: This ensures that the brake parts fit correctly in the braking system using precise measurements.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Conductivity Tests: These tests check how well the material handles high temperatures and stops brake fade.
Balancing Tests: These find and fix imbalances to stop vibrations when braking.
Fatigue Testing: This checks how durable the material is under long use and repeated stress.
Corrosion Resistance Testing: This simulates tough conditions to see how well it resists rust.
Impact and Load Testing: This tests how well the material can handle sudden forces and heavy weights.
By focusing on good materials and thorough testing, you can make sure your brake parts give the performance and reliability needed for safe driving.
Quality Control for Brake Safety

Inspection Methods
You need to make sure that brake parts are safe and high quality. Different inspection methods help with this. Here are some main inspection techniques used for OEM brake components:
Product Requirements: Check that the prototype matches the drawings and client needs.
Material and Construction: Make sure only top-quality materials are used and tested.
Weight and Dimensions: Follow the client’s checklist for correct weighing and measuring.
Colour: Compare the colour to a sample from mass production.
Functionality: Test how the device works to ensure it operates correctly.
Markings and Labelling: Check that labels are accurate to confirm compliance.
Besides these methods, advanced testing techniques help find defects in brake parts:
Visual Testing (VT): Quickly spots surface defects but depends on the inspector’s skill.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Uses sound waves to find internal problems, good for deep checks.
Radiographic Testing (RT): Creates images of inside structures using X-rays to show cracks and holes.
Eddy Current Testing (ET): Finds surface or near-surface defects in conductive materials.
These inspection methods are very important for keeping brake parts reliable over time. By doing thorough testing, manufacturers can make sure their products are safe and work well.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is very important in making brake parts. As safety features become more important, car makers work on better processes. Here are some key parts of continuous improvement in OEM brake manufacturing:
A complete quality control system is set up.
Tests include Material Analysis, Hardness Testing, Dimensional and Fit Checks, Dynamic Balancing, and Performance Testing.
Strict quality assurance steps are followed at every stage of production.
By using real-time location systems (RTLS) and special end-of-line testing software, manufacturers can improve their inspection processes. This leads to better quality assurance and encourages a culture of continuous improvement.
Statistical process control (SPC) is also important for reducing defects. By checking key operations, manufacturers can make sure they meet strict safety and performance standards. In brake part assembly, SPC uses Pareto analysis to find common defects. By focusing on these problems, teams can take specific actions that greatly lower the overall defect rate.
Following Industry Rules
Rules You Need to Know
You need to know the rules that apply to brake parts. These rules make sure your brakes work safely and well. Some important rules are:
Rule | What It Means |
|---|---|
Sets rules for how brakes should work, like stopping distance and how brake force is shared. | |
FMVSS No. 135 | Lists minimum performance rules for brakes to keep them safe. |
ISO 26262 | Focuses on the safety of electrical systems in cars, giving guidelines for making and testing brake systems. |
These rules are very important for designing and testing brake parts. They help makers create products that meet safety needs and improve how vehicles perform. As rules get stricter, you can expect better braking features, like anti-lock brakes (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC).
Why Certifications Matter
Certifications are important for making sure brake parts are safe and high quality. They show that products meet industry rules. Here are some key certifications that car makers value:
Certification | What It Means |
|---|---|
A European rule for replacement brake linings, important for companies that export. | |
AMECA | A North American certification needed to sell in the U.S. aftermarket. |
IATF 16949 | A certification for automotive quality management, showing serious manufacturers. |
ISO 14001 | An environmental certification that shows a commitment to eco-friendly production. |
Getting these certifications makes your product more trustworthy to customers. A survey found that 68% of brake material makers spend over 15% of their research budgets on getting certified. This shows how important following the rules is in the market. Not following the rules can lead to legal issues, product recalls, and harm to a brand’s reputation.
Not following the rules can seriously hurt a company’s money, reputation, and future. That’s why businesses must focus on compliance and set up strong systems to reduce these risks.
By following industry rules and getting the right certifications, you can make sure your brake parts are safe and reliable for customers.
Innovation and Customer Feedback
New Technologies
Using new technologies in brake design makes them work better and last longer. Here are some recent changes in OEM brake parts:
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Methods like additive manufacturing and precision composites make brake parts better.
Robotics and Automation: These tools help make production more accurate and efficient.
IoT Sensors: Smart factories use IoT sensors to check quality in real-time.
AI-Driven Systems: These systems can predict how well brakes will work, ensuring they stop effectively.
These improvements lead to better braking materials, like carbon ceramic brakes, which are lighter, stronger, and stop faster. Also, electronic brake technology, such as ABS and EBD, helps with control and stability when braking.
Customer Insights
Hearing what customers say is very important for improving brake parts. Manufacturers can learn from user experiences to make better products. Here are some key points:
Performance Needs: Customers want better stopping power and longer-lasting brakes.
Environmental Concerns: Many people prefer eco-friendly materials and methods that lower emissions.
Customization: Drivers like features that let them adjust their braking experience.
By focusing on these points, manufacturers can create high-performance, eco-friendly brake materials. Ongoing investment in research and development helps companies meet market needs and stay ahead in the car industry.
Remember, innovation is not just about technology; it’s about understanding what customers need and providing solutions that go beyond their expectations.
In conclusion, making sure OEM brake parts are reliable depends on strong quality control. You get better brake parts that improve safety and performance. Here are the main points:
Good brake parts give you better stopping power and shorter stopping distances.
Reliable brake pads and rotors stop brake fade, keeping brakes working well.
Thorough quality control steps, like checking raw materials and final tests, are key for safety.
Continuous improvements in quality control, like strict management systems and real-time checks, make brake parts even more reliable. By focusing on these practices, manufacturers can provide products you can trust for your safety while driving.
FAQ
What materials are best for brake components?
The best materials for brake parts are high-quality ones like ceramic and semi-metallic compounds. They perform well, last a long time, and resist heat, making sure your brakes are safe and reliable.
How often should I inspect my brake system?
You should check your brake system at least once a year or every 12,000 miles. Regular inspections help find wear and tear, keeping your brakes safe and working well.
What certifications should I look for in brake parts?
Look for certifications like ECE R90 and IATF 16949. These show that the brake parts meet safety and quality rules, giving you confidence in your vehicle’s performance.
How can I improve my vehicle’s braking performance?
You can improve braking by using high-quality brake pads, making sure they are installed correctly, and keeping up with brake maintenance. Upgrading to better brake parts can also help a lot.
What should I do if I notice unusual noises from my brakes?
If you hear strange noises like squeaking or grinding, you should get your brakes checked right away. These sounds usually mean there is wear or damage, which can put your safety at risk.